Η Αστρονομική Εικόνα της Ημέρας από τη NASA
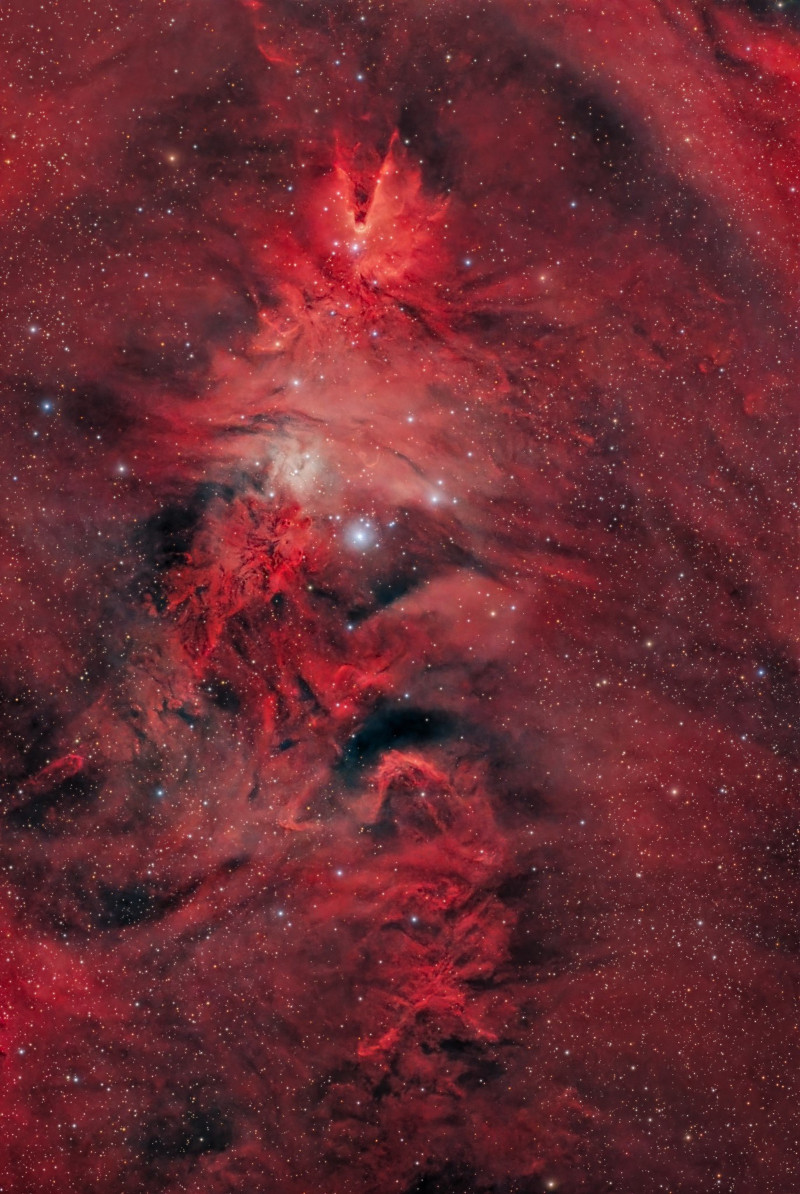
Unicorn, Fox Fur and Christmas Tree
25/12/2025
A star forming region cataloged as NGC 2264, this beautiful but complex arrangement of interstellar gas and dust is about 2,700 light-years distant in the faint but fanciful constellation Monoceros, the Unicorn. Seen toward the celestial equator and near the plane of our Milky Way galaxy, the seasonal skyscape mixes reddish emission nebulae excited by energetic light from newborn stars with dark interstellar dust clouds. Where the otherwise obscuring dust clouds lie close to the hot, young stars, they also reflect starlight, forming blue reflection nebulae. In fact, bright variable star S Monocerotis is immersed in a blue-tinted haze near center. Arrayed with a simple triangular outline above S Monocerotis, the stars of NGC 2264 are popularly known as the Christmas Tree star cluster. Carved by energetic starlight, the Cone Nebula sits upside down at the apex of this cosmic Christmas tree while the dusty, convoluted pelt of glowing gas and dust under the tree is called the Fox Fur Nebula. This rich telescopic frame spans about 1.5 degrees or 3 full moons on the sky top to bottom, covering nearly 80 light-years at the distance of NGC 2264.
Copyright: Michael Kalika
Προηγούμενες Αστρονομικές Εικόνες της Ημέρας από τη NASA
Total Eclipse and Comets
17/04/2024
Not one, but two comets appeared near the Sun during last week's total solar eclipse. The expected comet was Comet 12P/Pons-Brooks, but it was disappointingly dimmer than many had hoped. However, relatively unknown Comet SOHO-5008 also appeared in long duration camera exposures. This comet was the 5008th comet identified on images taken by ESA & NASA's Sun-orbiting SOHO spacecraft. Likely much smaller, Comet SOHO-5008 was a sungrazer which disintegrated within hours as it passed too near the Sun. The featured image is not only unusual for capturing two comets during an eclipse, but one of the rare times that a sungrazing comet has been photographed from the Earth's surface. Also visible in the image is the sprawling corona of our Sun and the planets Mercury (left) and Venus (right). Of these planets and comets, only Venus was easily visible to millions of people in the dark shadow of the Moon that crossed North America on April 8. Solar Eclipse Imagery: Notable Submissions to APOD
Copyright: Lin Zixuan (Tsinghua U.)
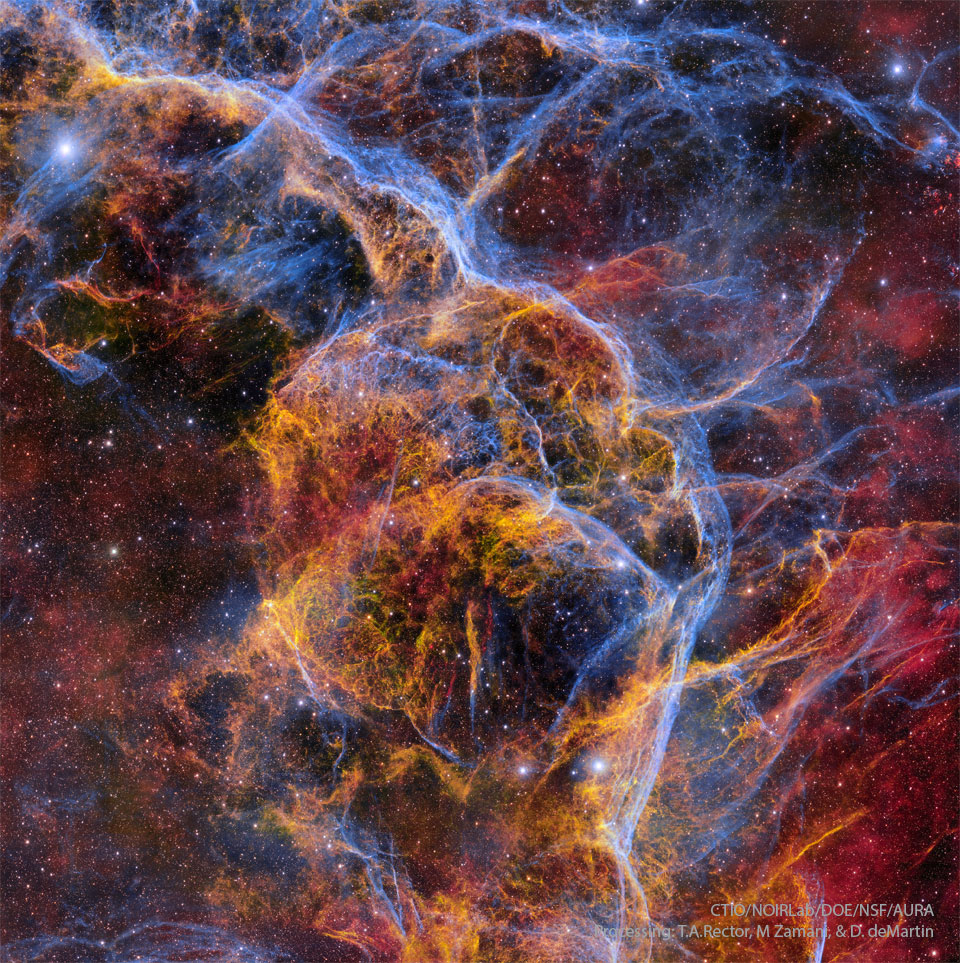
Filaments of the Vela Supernova Remnant
16/04/2024
The explosion is over, but the consequences continue. About eleven thousand years ago, a star in the constellation of Vela could be seen to explode, creating a strange point of light briefly visible to humans living near the beginning of recorded history. The outer layers of the star crashed into the interstellar medium, driving a shock wave that is still visible today. The featured image captures some of that filamentary and gigantic shock in visible light. As gas flies away from the detonated star, it decays and reacts with the interstellar medium, producing light in many different colors and energy bands. Remaining at the center of the Vela Supernova Remnant is a pulsar, a star as dense as nuclear matter that spins around more than ten times in a single second. Monday's Eclipse Imagery: Notable Submissions to APOD
Copyright: NASA
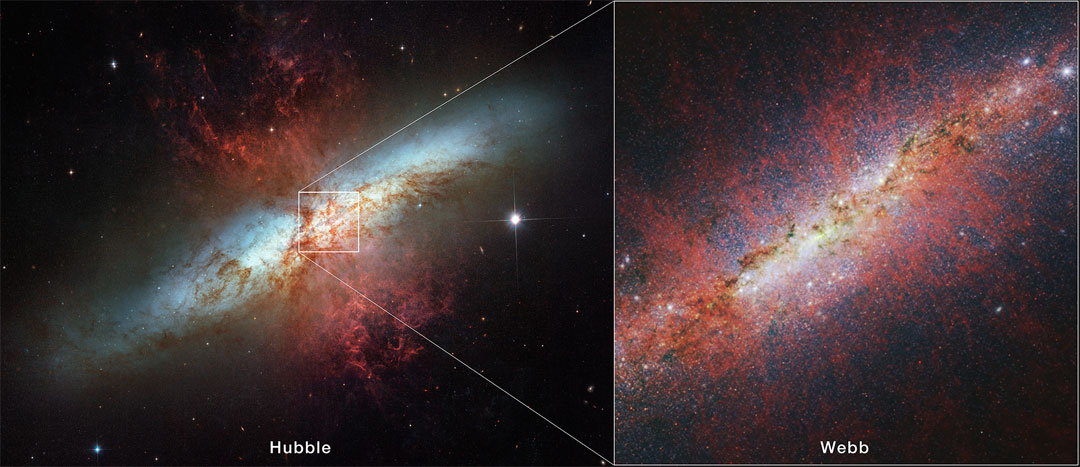
The Cigar Galaxy from Hubble and Webb
15/04/2024
Something strange happened to this galaxy, but what? Known as the Cigar Galaxy and cataloged as M82, red glowing gas and dust are being cast out from the center. Although this starburst galaxy was surely stirred up by a recent pass near its neighbor, large spiral galaxy M81, this doesn't fully explain the source of the red-glowing outwardly expanding gas and dust. Evidence indicates that this material is being driven out by the combined emerging particle winds of many stars, together creating a galactic superwind. In the featured images, a Hubble Space Telescope image in visible light is shown on the left, while a James Webb Space Telescope image of the central region in infrared light is shown on the right. Detailed inspection of the new Webb image shows, unexpectedly, that this red-glowing dust is associated with hot plasma. Research into the nature of this strange nearby galaxy will surely continue. Total Eclipse Imagery: Notable Submissions to APOD
Copyright: NASA
How a Total Solar Eclipse Ended
14/04/2024
How does a total solar eclipse end? Yes, the Moon moves out from fully blocking the Sun, but in the first few seconds of transition, interesting things appear. The first is called a diamond ring. Light might stream between mountains or through relative lowlands around the Moon's edge, as seen from your location, making this sudden first light, when combined with the corona that surrounds the Moon, look like a diamond ring. Within seconds other light streams appear that are called, collectively, Bailey's beads. In the featured video, it may seem that the pink triangular prominence on the Sun is somehow related to where the Sun begins to reappear, but it is not. Observers from other locations saw Bailey's beads emerge from different places around the Moon, away from the iconic triangular solar prominence visible to all. The video was captured with specialized equipment from New Boston, Texas, USA on April 8, 2024. Solar Eclipse Imagery: Notable Submissions to APOD
Copyright: David Duarte
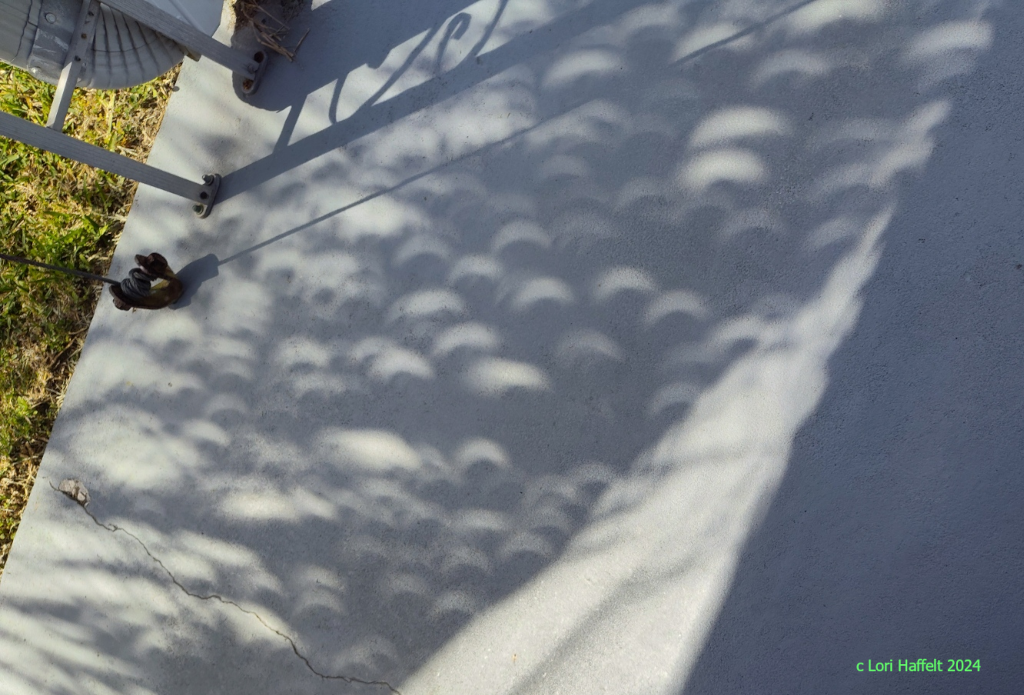
Palm Tree Partial Eclipse
13/04/2024
Only those along the narrow track of the Moon's shadow on April 8 saw a total solar eclipse. But most of North America still saw a partial eclipse of the Sun. From Clearwater, Florida, USA this single snapshot captured multiple images of that more widely viewed celestial event without observing the Sun directly. In the shade of a palm tree, criss-crossing fronds are projecting recognizable eclipse images on the ground, pinhole camera style. In Clearwater the maximum eclipse phase was about 53 percent. Solar Eclipse Imagery: Notable Submissions to APOD
Copyright: Lori Haffelt
Total Totality
12/04/2024
Baily's beads often appear at the boundaries of the total phase of an eclipse of the Sun. Pearls of sunlight still beaming through gaps in the rugged terrain along the lunar limb silhouette, their appearance is recorded in this dramatic timelapse composite. The series of images follows the Moon's edge from beginning through the end of totality during April 8's solar eclipse from Durango, Mexico. They also capture pinkish prominences of plasma arcing high above the edge of the active Sun. One of the first places in North America visited by the Moon's shadow on April 8, totality in Durango lasted about 3 minutes and 46 seconds. Solar Eclipse Imagery: Notable Submissions to APOD
Copyright: Daniel Korona
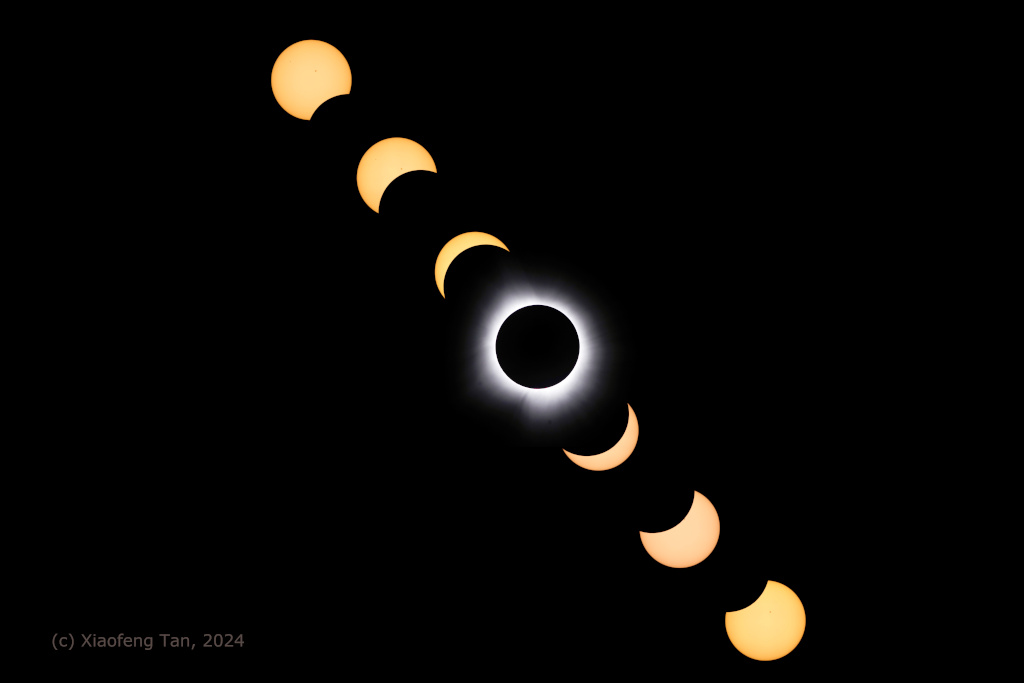
Eclipse in Seven
11/04/2024
Start at the upper left above and you can follow the progress of April 8's total eclipse of the Sun in seven sharp, separate exposures. The image sequence was recorded with a telescope and camera located within the narrow path of totality as the Moon's shadow swept across Newport, Vermont, USA. At center is a spectacular view of the solar corona. The tenuous outer atmosphere of the Sun is only easily visible to the eye in clear dark skies during the total eclipse phase. Seen from Newport, the total phase for this solar eclipse lasted about 3 minutes and 26 seconds. Monday's Eclipse Imagery: Notable Submissions to APOD
Copyright: April 8's
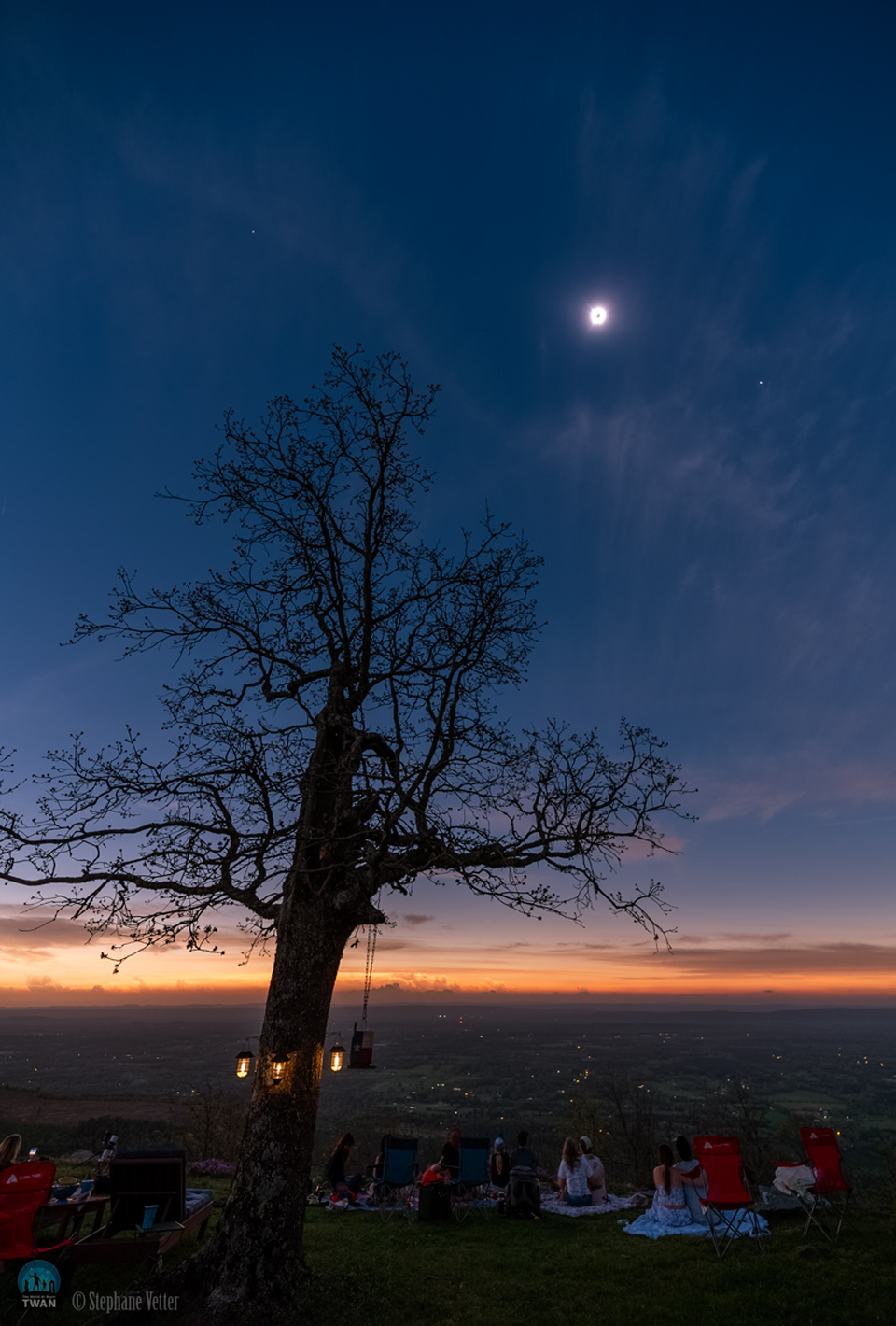
Planets Around a Total Eclipse
10/04/2024
What wonders appear when the Moon blocks the Sun? For many eager observers of Monday’s total eclipse of the Sun, the suddenly dark sky included the expected corona and two (perhaps surprise) planets: Venus and Jupiter. Normally, in recent days, Venus is visible only in the morning when the Sun and Jupiter are below the horizon, while Jupiter appears bright only in the evening. On Monday, though, for well-placed observers, both planets became easily visible during the day right in line with the totally eclipsed Sun. This line was captured Monday afternoon in the featured image from Mount Nebo, Arkansas, USA, along with a line of curious observers — and a picturesque tree. Monday's Eclipse Imagery: Notable Submissions to APOD
Copyright: NASA
Η Αστρονομική Εικόνα της Ημέρας από τη NASA (NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day) είναι μια δωρεάν υπηρεσία που παρέχει καθημερινά μια εντυπωσιακή εικόνα από το σύμπαν, την λήψη της οποίας έχει πραγματοποιήσει κάποιος από τους αστρονόμους της NASA ή από κάποιον από τους δορυφόρους ή τα τηλεσκόπια που η NASA λειτουργεί. Οι εικόνες που εμφανίζονται καλύπτουν μια ευρεία γκάμα από θέματα, συμπεριλαμβανομένων των αστερισμών, των γαλαξιών, των πλανητικών συστημάτων, των κομητών, των αστρικών σωμάτων και των παρατηρητηρίων. Κάθε εικόνα συνοδεύεται από μια σύντομη εξήγηση και πληροφορίες σχετικά με το τι παρατηρείται στην εικόνα.