Η Αστρονομική Εικόνα της Ημέρας από τη NASA
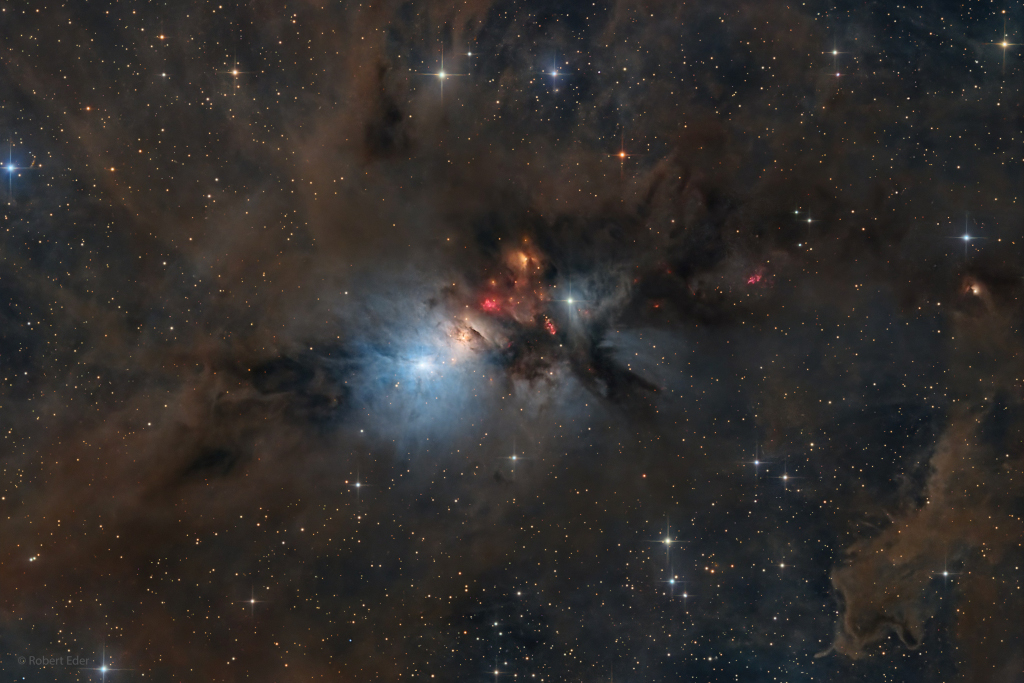
NGC 1333: Stellar Nursery in Perseus
30/01/2026
NGC 1333 is seen in visible light as a reflection nebula, dominated by bluish hues characteristic of starlight reflected by interstellar dust. A mere 1,000 light-years distant toward the heroic constellation Perseus, it lies at the edge of a large, star-forming molecular cloud. This telescopic close-up spans over two full moons on the sky or just over 15 light-years at the estimated distance of NGC 1333. It shows details of the dusty region along with telltale hints of contrasty red emission from Herbig-Haro objects, jets and shocked glowing gas emanating from recently formed stars. In fact, NGC 1333 contains hundreds of stars less than a million years old, most still hidden from optical telescopes by the pervasive stardust. The chaotic environment may be similar to one in which our own Sun formed over 4.5 billion years ago.
Copyright: Robert Eder
Προηγούμενες Αστρονομικές Εικόνες της Ημέρας από τη NASA
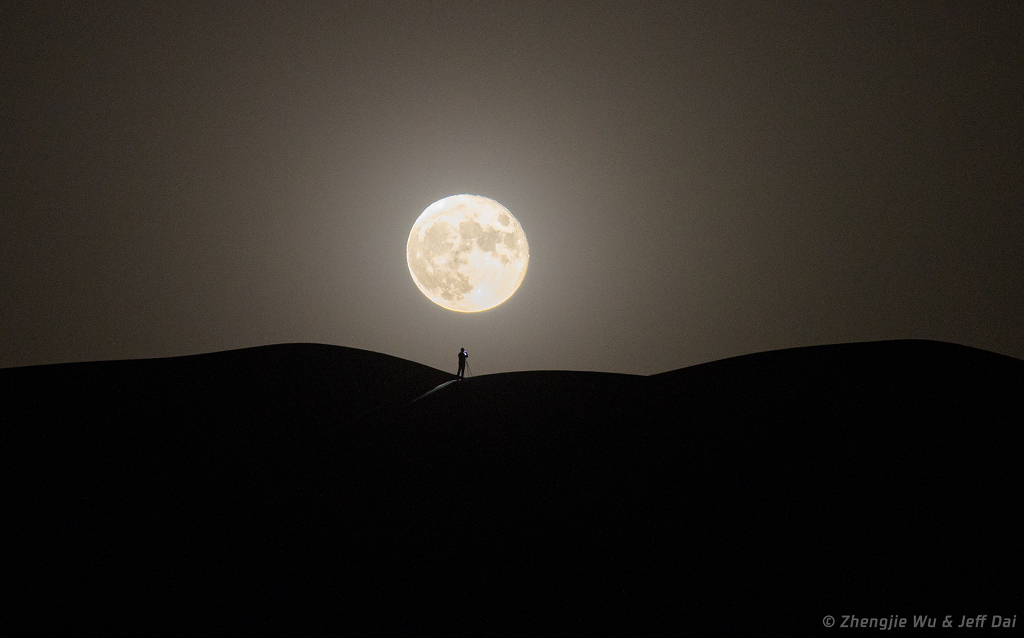
Full Moonlight
03/01/2026
The Full Moon is the brightest lunar phase, and tonight you can stand in the light of the first Full Moon of 2026. In fact, the Moon's full phase occurs on January 3 at 10:03 UTC, while only about 7 hours later planet Earth reaches its 2026 perihelion, the closest point in its elliptical orbit around the Sun, at 17:16 UTC. January's Full Moon was also not far from its own perigee, or closest approach to planet Earth. For this lunation the Moon's perigee was on January 1 at 21:44 UTC. You can also spot planet Jupiter, near its brightest for 2026 and close on the sky to the Full Moon tonight. But while you're out skygazing don't forget to look for rare, bright fireballs from the Quadrantid meteor shower.
Copyright: Jeff Dai
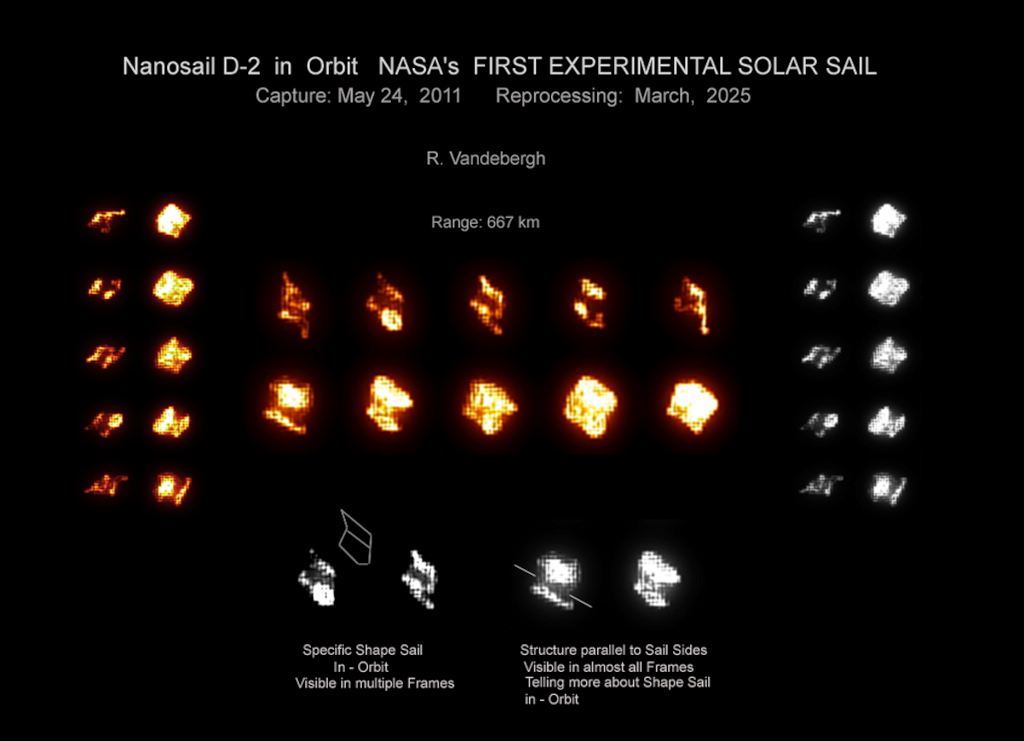
NanoSail-D2
02/01/2026
In 2011, on January 20, NASA's NanoSail-D2 unfurled a very thin and very reflective 10 square meter sail becoming the first solar sail spacecraft in low Earth orbit. Often considered the stuff of science fiction, sailing through space was suggested 400 years ago by astronomer Johannes Kepler, who had observed comet tails blown by the solar wind. But modern solar sail spacecraft designs, like NanoSail-D2, Japan's interplanetary spacecraft IKAROS, or the Planetary Society's Lightsail A, rely on the small but continuous pressure from sunlight itself for thrust. Glinting in the sunlight as it circled planet Earth, NanoSail-D2's solar sail was periodically bright and visible to the eye. These remarkably detailed images were captured by manually tracking the orbiting solar sail spacecraft with a small telescope.
Copyright: Ralf Vandebergh
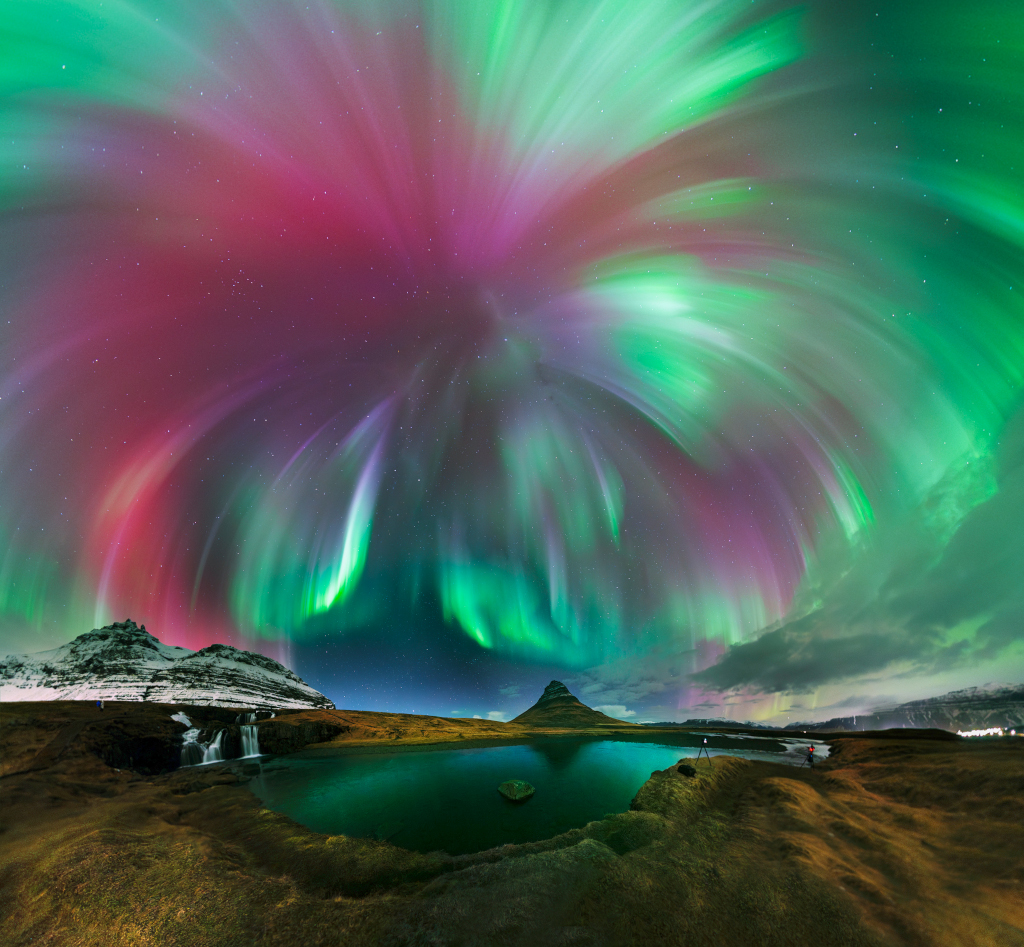
Auroral Corona
01/01/2026
Cycle 25 solar maximum made 2025 a great year for aurora borealis (or aurora australis) on planet Earth. And the high level of solar activity should extend into 2026. So, while you're celebrating the arrival of the new year, check out this spectacular auroral display that erupted in starry night skies over Kirkjufell, Iceland. The awesome auroral corona, energetic curtains of light streaming from directly overhead, was witnessed during a strong geomagnetic storm triggered by intense solar activity near the March 2025 equinox. This northland and skyscape captures the evocative display in a 21 frame panoramic mosaic.
Copyright: Roi Levi
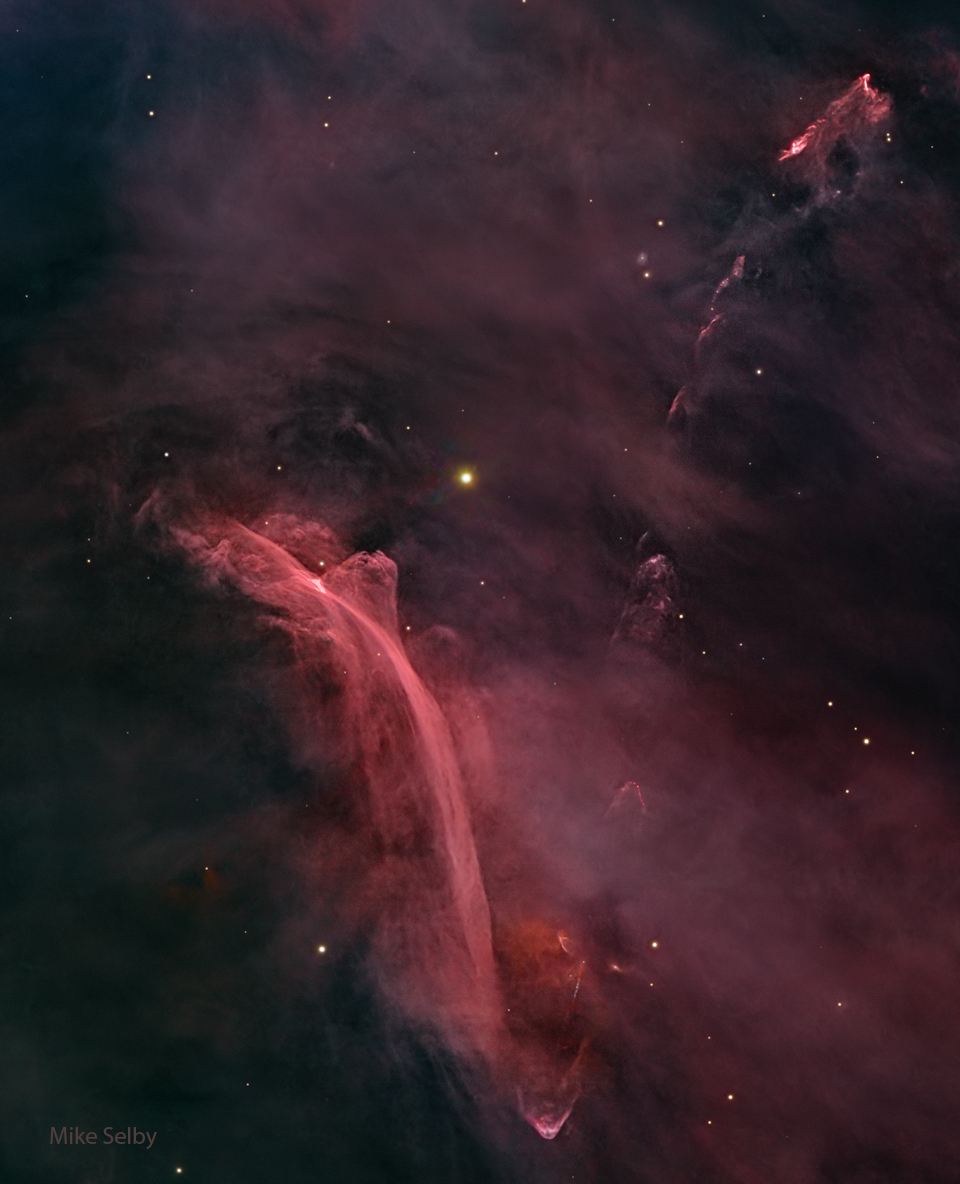
HH-222: The Waterfall Nebula
31/12/2025
What created the Waterfall Nebula? The origin is still being researched. The structure, officially designated Herbig-Haro 222, appears in the region of NGC 1999 in the Great Orion Molecular Cloud complex. The elongated gaseous stream stretches about ten light years but appears similar to a long waterfall on Earth. Recent observations indicate that HH-222 is likely a gigantic gaseous bow shock, similar to a wave of water caused by a fast-moving ship. The origin of this shock wave is thought to be a jet outflow from the multiple star system V380 Orionis off the lower left of the frame. Therefore, gas does not flow along the waterfall, but rather the entire structure moves toward the upper right. The Waterfall Nebula lies about 1,500 light years away toward the constellation of Orion. The featured image was captured earlier this month from El Sauce Observatory in Chile. Jigsaw Nebula: Astronomy Puzzle of the Day
Copyright: Mike Selby
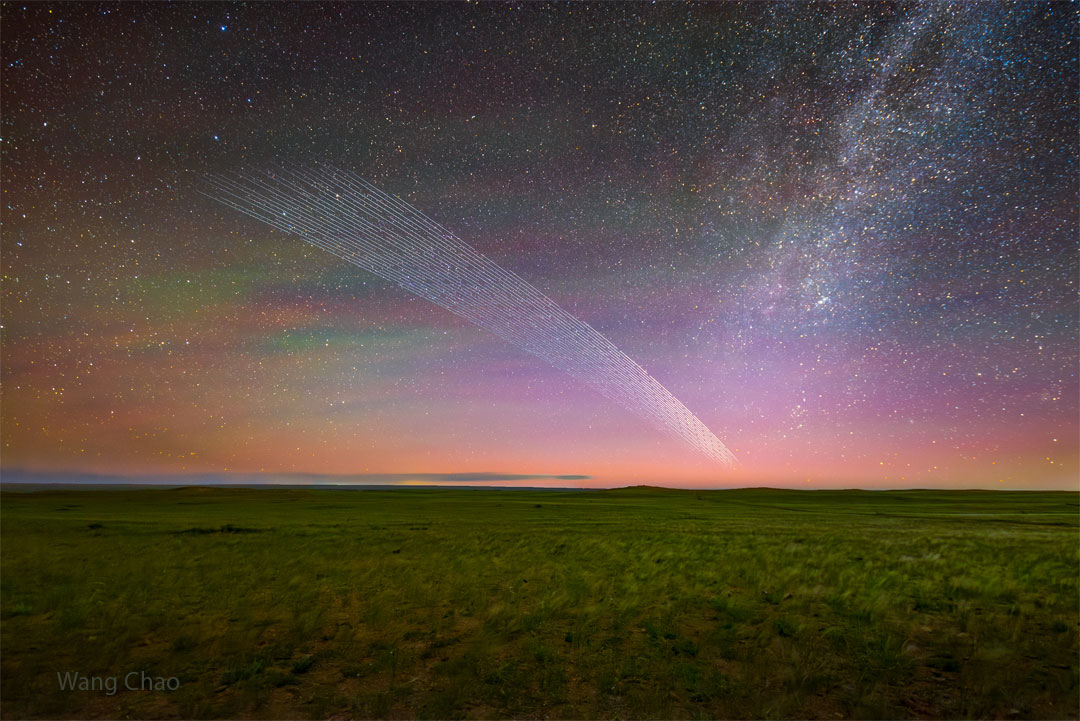
An Artificial Comet
30/12/2025
Yes, but can your comet tail do this? No, and what you are seeing is not the tail of a comet. The picture features a cleverly overlayed time-lapse sequence of a group of satellites orbiting Earth together in June. Specifically, these are Starlink communications satellites in low Earth orbit reflecting back sunlight before sunrise to Inner Mongolia, China. Although the satellites appear to the human eye as points, the 20-second-long camera exposures caused them to appear as short streaks. Currently there are over 9000 Starlinks in orbit, with more being launched nearly every week. Other satellite constellations are also being planned. Explore the Universe: Random APOD Generator
Copyright: Wang Chao
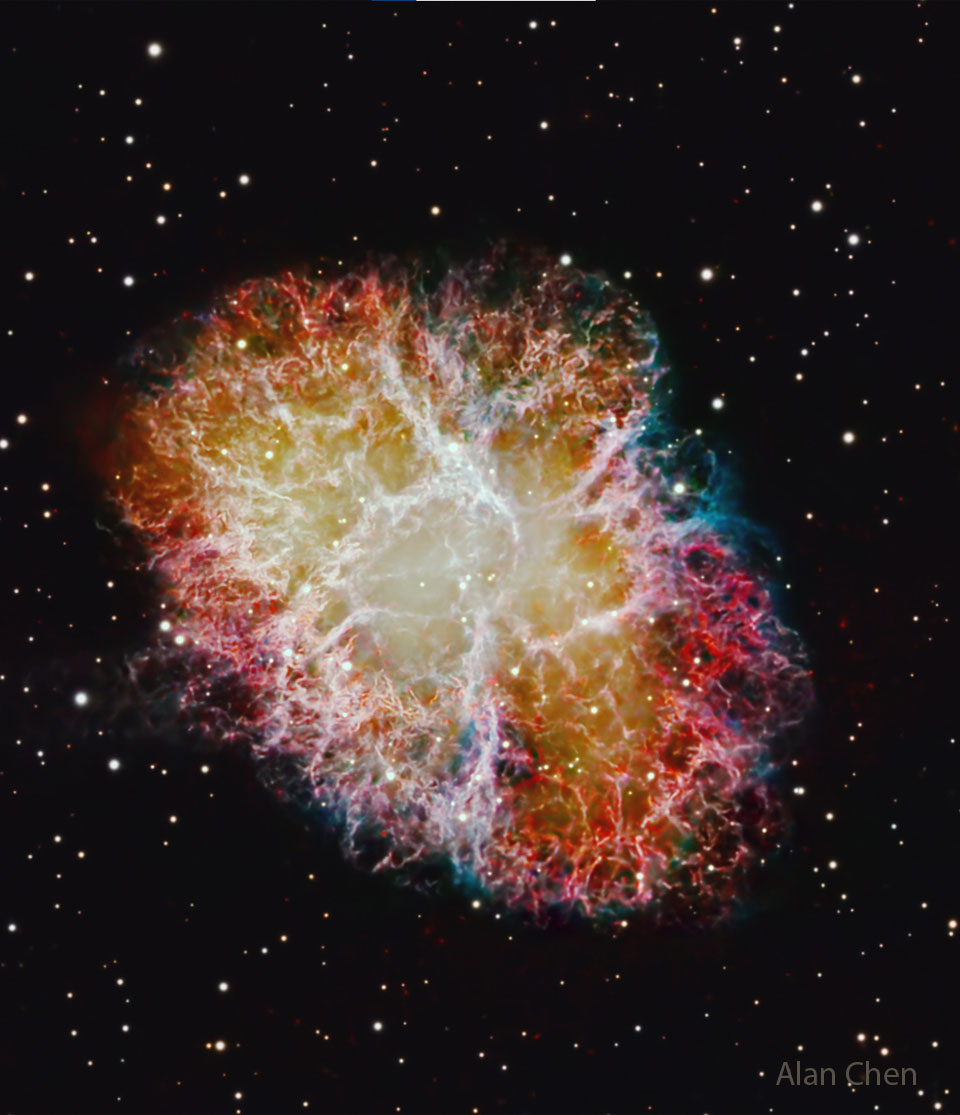
M1: The Crab Nebula
29/12/2025
This is the mess that is left when a star explodes. The Crab Nebula, the result of a supernova seen in 1054 AD, is filled with mysterious filaments. The filaments are not only tremendously complex but appear to have less mass than expelled in the original supernova and a higher speed than expected from a free explosion. The featured image was taken by an amateur astronomer in Leesburg, Florida, USA over three nights last month. It was captured in three primary colors but with extra detail provided by specific emission by hydrogen gas. The Crab Nebula spans about 10 light years. In the Nebula's very center lies a pulsar: a neutron star as massive as the Sun but with only the size of a small town. The Crab Pulsar rotates about 30 times each second. Explore the Universe: Random APOD Generator
Copyright: Alan Chen
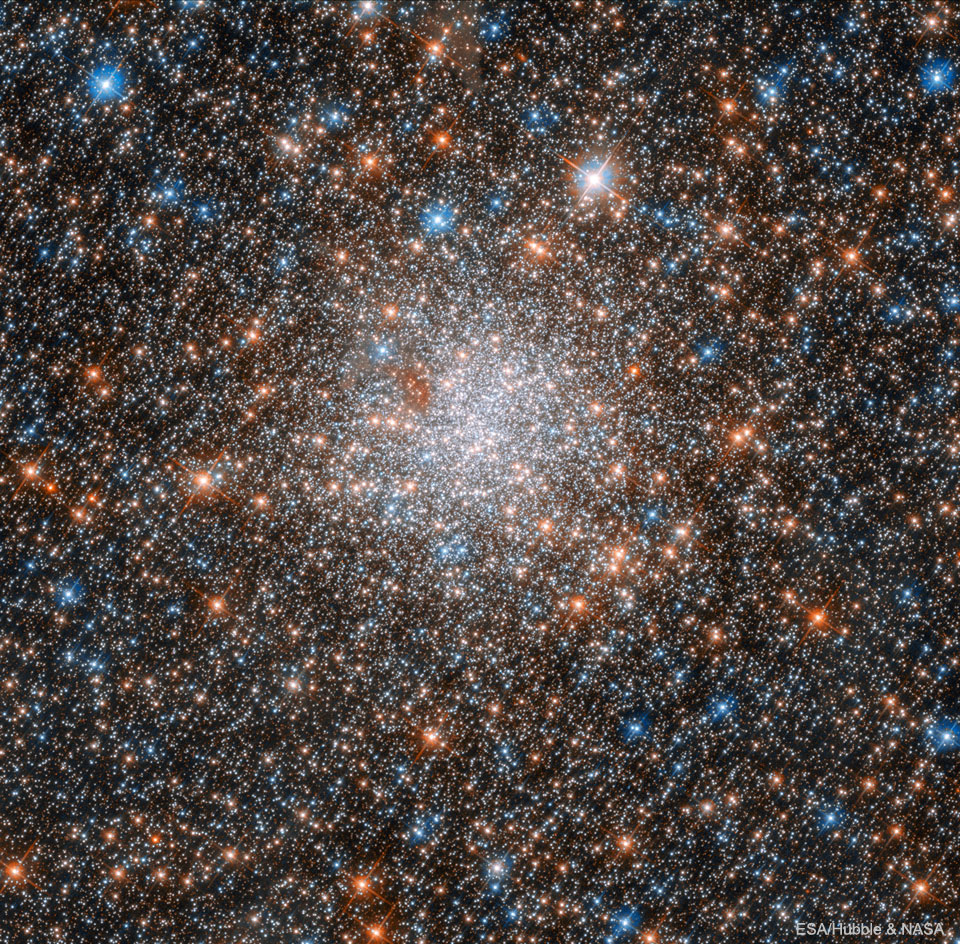
NGC 1898: Globular Cluster in the Large Magellanic Cloud
28/12/2025
Jewels don't shine this bright -- only stars do. And almost every spot in this jewel-box of an image from the Hubble Space Telescope is a star. Now, some stars are more red than our Sun, and some more blue -- but all of them are much farther away. Although it takes light about 8 minutes to reach Earth from the Sun, NGC 1898 is so far away that it takes light about 160,000 years to get here. This huge ball of stars, NGC 1898, is called a globular cluster and resides in the central bar of the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) -- a satellite galaxy of our Milky Way Galaxy. The featured multi-colored image includes light from the infrared to the ultraviolet and was taken to help determine if the stars of NGC 1898 all formed at the same time or at different times. There are increasing indications that most globular clusters formed stars in stages, and that, in particular, stars from NGC 1898 formed shortly after ancient encounters with the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC) and our Milky Way Galaxy. Space Telescopes Live: Where are Hubble and Webb looking right now?
Copyright: NASA
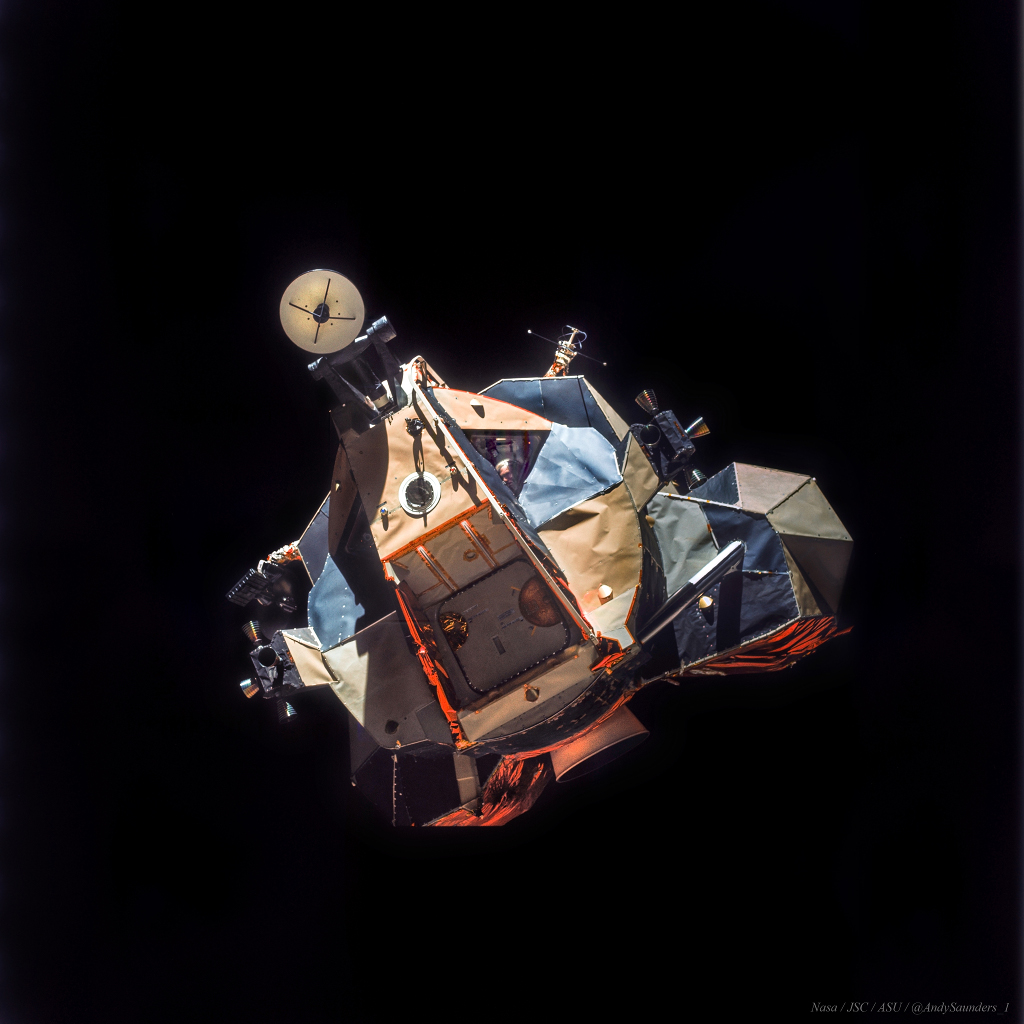
Apollo 17's Moonship
27/12/2025
Awkward and angular looking, Apollo 17's lunar module Challenger was designed for flight in the near vacuum of space. Digitally enhanced and reprocessed, this picture taken from Apollo 17's command module America shows Challenger's ascent stage in lunar orbit. Small reaction control thrusters are at the sides of the moonship with the bell of the ascent rocket engine underneath. The hatch that allowed access to the lunar surface is seen at the front, with a round radar antenna at the top. Mission commander Gene Cernan is clearly visible through the triangular window. This spaceship performed gracefully, landing on the Moon and returning the Apollo astronauts to the orbiting command module in December of 1972. So where is Challenger now? While its descent stage remains at the Apollo 17 landing site in the Taurus-Littrow valley, the ascent stage pictured was intentionally crashed nearby after being jettisoned from the command module prior to the astronauts' return to planet Earth.
Copyright: NASA
Η Αστρονομική Εικόνα της Ημέρας από τη NASA (NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day) είναι μια δωρεάν υπηρεσία που παρέχει καθημερινά μια εντυπωσιακή εικόνα από το σύμπαν, την λήψη της οποίας έχει πραγματοποιήσει κάποιος από τους αστρονόμους της NASA ή από κάποιον από τους δορυφόρους ή τα τηλεσκόπια που η NASA λειτουργεί. Οι εικόνες που εμφανίζονται καλύπτουν μια ευρεία γκάμα από θέματα, συμπεριλαμβανομένων των αστερισμών, των γαλαξιών, των πλανητικών συστημάτων, των κομητών, των αστρικών σωμάτων και των παρατηρητηρίων. Κάθε εικόνα συνοδεύεται από μια σύντομη εξήγηση και πληροφορίες σχετικά με το τι παρατηρείται στην εικόνα.